Filing incident reports is an essential part of improving the way your business operates. Comprehensive incident reporting boosts workplace safety, and it’s particularly important in dangerous fields such as construction, mining, or factory work.
From personal injuries to equipment failures, this guide will show you how to write an incident report effectively. You’ll also learn about the different types of incidents covered and get an example format that you can easily adapt to your organization.
What is an incident report?
Incident reports are the tools businesses use to take note of an incident – usually related to an accident or injury – in the workplace. It’s applicable for a variety of contexts. You can write one to address personal injuries, equipment malfunctions, health and safety issues, employee misconduct, and more.
You should always write an incident report as soon after observing the incident as possible. Usually, you’ll only use reports internally to correct whatever has gone wrong, but sometimes outside parties like insurance companies or stakeholders will need the information, so it is best to have it on hand quickly.
What is the purpose of an incident report?
A promptly written incident report is essential to improving conditions in the workplace. It will help you understand what has gone wrong, where the issue comes from, and what steps you need to take to resolve said issue.
Often you might not have been aware that anything was wrong without one of these reports, which illustrates how crucial they are. Incident reports are the first step to improving problematic conditions in the workplace, whether that means removing hazards, improving building security, or optimizing workflows.
In an industry with many safety risks, such as construction or mining, communicating any malfunctions or unsafe conditions as soon as possible is essential. That way, supervisors can put measures in place to prevent similar incidents from happening a second time.
Incident reports can lead to major changes in day-to-day operations. By pointing out areas that repeatedly cause problems, these reports show managers what they need to correct or do away with. It can also lead to new policies and regulations intended to protect workers.
Filing an incident report is a form of legal response to an issue. This is important because it underlines the urgency of response and provides a justification for acting as quickly as possible. And even though it is a legal matter, anyone in a company can write and submit incident reports.
Types of incidents to report
An incident is defined as any event or situation that:
- Disrupts or interferes with an organization
- Causes significant risk to members in an organization
- Has an impact on the operations of a workplace
- Is a source of negative media attention for the company.
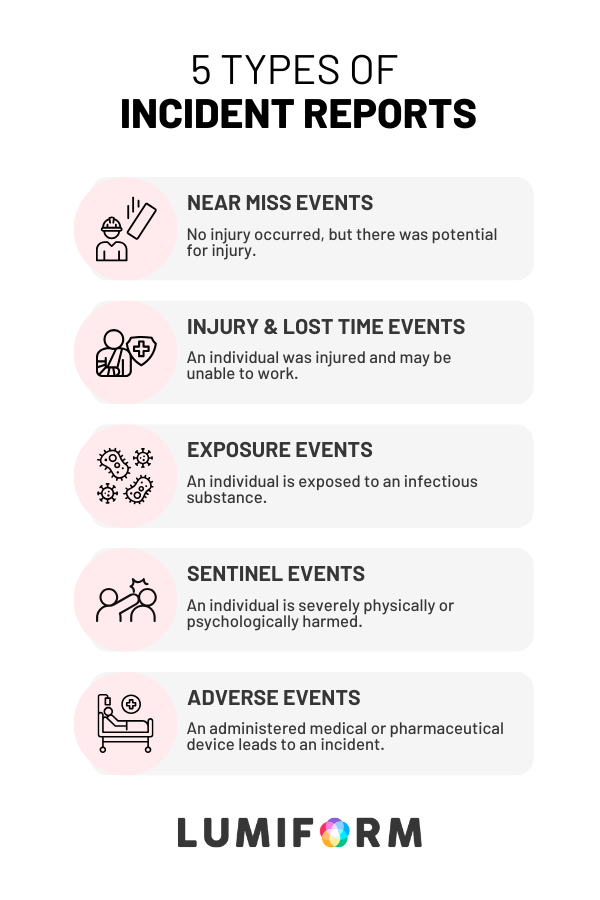
Though the criteria for classifying an incident are broad, there are 5 major categories they fall under:
Near-miss events
A near miss event is a situation in which damage or an accident could have happened, but were luckily avoided. Near misses indicate that things are unsafe regardless of whether someone was actually hurt.
Example: if a piece of equipment breaks and almost cuts a worker, the equipment would need fixing.
Injury and lost time
Injury and lost time events refer to cases where workers are injured and to cases where they are unable to work due to said injury. Any injury resulting from unsafe practices or equipment is grounds for a report, no matter how severe.
Example: A worker might break their leg because a wire snapped or burn themselves on a faulty stove.
Exposure incidents
Exposure incidents refer to an individual becoming exposed to infectious substances, such as blood. These events are most common in industries like healthcare, but could occur in any workplace. Exposure incidents are very serious, since they also impact public safety.
Example: A contaminated needle accidentally pricks an employee at a hospital.
Sentinel events
Sentinel events are occurrences that cause severe physical or psychological harm to employees or members of the public. These might be because of natural disasters, vehicles, malfunctioning equipment, or electrical or natural fires. They often prompt careful examination by outside professionals.
Example: In a hotel, a guest gets seriously injured because of faulty elevator equipment.
Adverse events
Adverse events are emergencies caused by an allergic reaction to a medical or pharmaceutical device. These devices are most common among hospital patients, which means it is especially important that adverse events are reported and avoided in the future.
Example: A patient develops unexpected swelling and difficulty breathing after using a newly fitted insulin pump.
How do you write incident reports?
When you are preparing an incident report, be sure to include all the facts relating to the situation, and remember that more detail is always better. The more specific you are about what happened, the easier it will be to take any required action. Preparing your incident reports is easier with the help of these sample incident report templates that we’ve curated at Lumiform.
No matter your industry, any incident report should contain:
- The location, date, and time of the incident.
- Details about the environment that may have contributed to the event, such as loose nails on the floor of a construction site.
- The names and positions of everyone involved, whether they were directly affected or not.
- A breakdown of any injuries. What sort of injury was sustained, how severe was it, and what exactly did the person injure?
- Details about who witnessed the event, if any witnesses were present, as well as their statements.
- An account of any treatment administered when the incident happened. Specify what medications, if any, were given.
- A record of any property or equipment damage sustained as a result of the incident.
- The actions of everyone involved at the exact moment of the incident. Mention where they were standing, how they were moving, and what they were doing while the incident occurred.
Each of these details needs to be accurate, objective, and comprehensive. An incident report should answer the what, why, where, and how of any occurrence. Including visuals, such as photos of the injury, machinery, or surrounding environment, helps communicate findings clearly.
Sample incident report format
What does a sample incident report look like? The specific content of these forms will vary according to your industry – a construction site report will highlight different factors than an incident report filed at a daycare – but the what, why, where, and how of the incident will always be covered.
Incident reporting generally starts with an introduction. This is where you name all the people involved in the incident, the date, time, and location it occurred, and include a quick summary of the event.
From there, you can move into the body of your report. Expand on the quick summary in your introduction and provide the full context of the incident. From start to finish, go through each stage of the incident. Make sure to be specific when mentioning names and locations.
When concluding your incident report, describe how the situation was resolved. If it was unable to be resolved, explain why. What is needed for finding a solution that is not available? This will make your next steps clearer.
Finally, remember to include who completed the incident report and when it was completed. This helps improve record keeping and establishes accountability. Any photos you can include as evidence also make the incident report more useful.
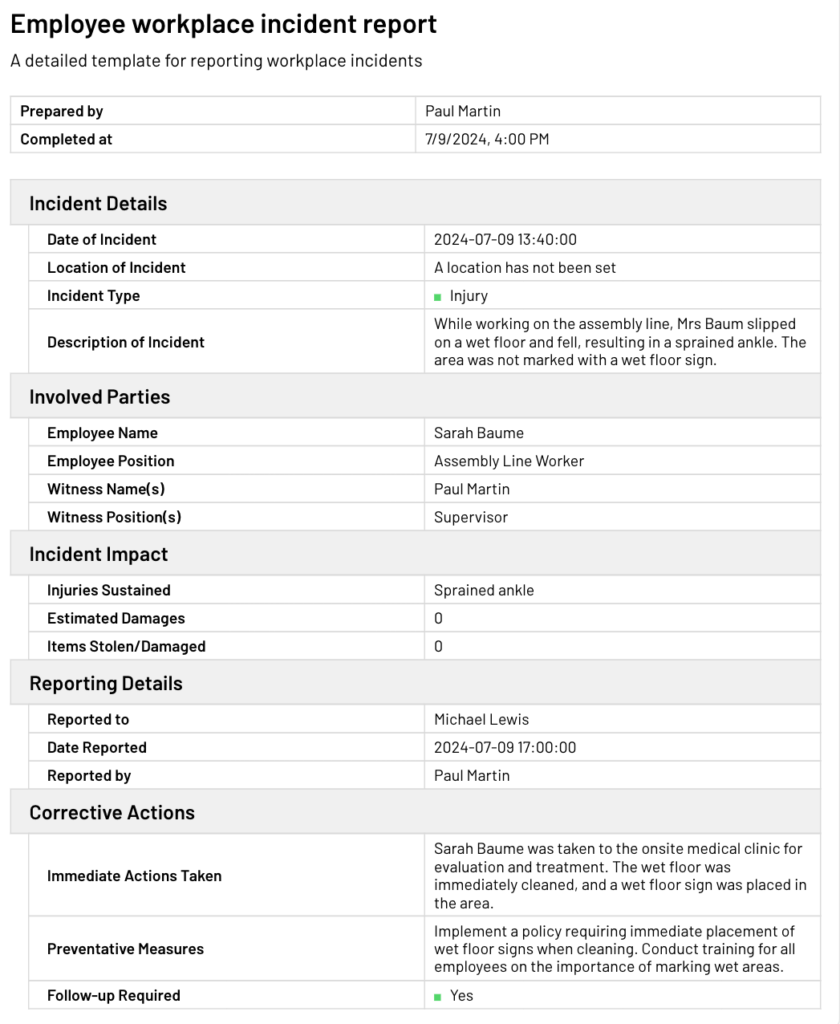
What questions should I cover in a sample incident report?
Each section of your incident report needs to answer specific questions. Here is a template where you see the sorts of questions included in a workplace incident report.
Fundamentals of the incident
In the beginning of any report, your goal is to answer the fundamentals of what happened and who it happened to. So you might ask questions like:
- Who was involved with the incident?
- Where specifically did the incident take place?
- Was anyone injured? If so, who?
- Was there any property or equipment damage? If so, what was damaged?
- What task was being performed by those involved?
Your goal is to determine the people involved, the work associated with the incident, and the general outcome.
Details about the damage and cause
The body of your report looks more closely at who was damaged, how badly, and what led to their accident. You want to know both how affected individuals are impacted currently and how things could change in the future. In case there was damage to an individual or to the premises, provide photos to illustrate what happened.
Sample incident report questions to ask in this section include:
- What equipment was in use at the time of the incident?
- Is that equipment functioning properly? If not, what is wrong with it?
- What type of injury was sustained? How severe was the injury?
- Will this injury prevent them from working?
- What led to the incident or injury?
- How severe was the damage to property?
Witness accounts
It is also important to determine if there were any witnesses to the incident. For one thing, they might have more context or details to add. For another, knowing that witnesses to an incident could have prevented or mitigated that incident may lead to new policies in the workplace.
Witness testimony can also be useful in determining whether the affected individual’s behavior played a role in the incident.
Resolution and next steps
Finally, note down how the event was resolved, and what steps to take in the future to avoid similar incidents. It might also be the case that nothing was resolved, which is also important to mention.
In this final section, you would ask questions such as:
- What was the response to the incident?
- Was any first aid administered?
- Is the cause of the incident clear? If yes, what caused it?
- Has the cause of the incident been fixed?
- wWhat could have prevented this incident?
After your incident report is complete, submit it for investigation. That investigation will look at the costs associated with the incident and determine the root cause, so that regulatory requirements are followed more closely in the future.
Streamline incident reporting with Lumiform
Timely completion of incident reports not only helps understand what issues are present in the workplace, but it also vastly improves record keeping in an organization. Lumiform makes this record keeping much easier, by saving you time and resources.
Instead of using pen and paper for incident reporting, use one of our digital templates that you can fill out in minutes. And once you have, you can easily download your results, assign corrective actions directly from the platform, and even track trends with data analytics.
Try Lumiform for free today and see how it simplifies reporting while driving real results!