Legionella, a naturally occurring bacterium, can be a serious threat to your business environment. It can lead to Legionnaires’ disease, a severe pneumonia affecting individuals with weakened immune systems. In this guide, you’ll find essential regional risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
Explore real-world case studies where manufacturing firms, institutions, and schools have successfully addressed outbreaks with innovative treatments and comprehensive controls.
Understanding Legionella and its risks
Legionella bacteria are recognized as a significant health concern due to their ability to thrive in certain water environments. The risks associated with Legionella are influenced by various factors that promote their growth and spread.
The following conditions are known to increase the risk of Legionella growth:
- Water Temperature: Optimal growth occurs in water temperatures between 25-45°C (77-113°F).
- Stagnation: Conditions such as dead-end pipes, infrequently used fixtures, and poorly flushed systems are conducive to stagnant water, which supports bacterial proliferation.
- Nutrients: The presence of biofilms, scale, rust, and organic matter is known to provide nutrients essential for Legionella growth.
- Aeration: Aerosols produced by showers, faucets, and cooling towers are capable of dispersing Legionella bacteria, heightening the risk of exposure.
Understanding these factors allows for the implementation of measures to reduce the risks associated with Legionella in water systems, thereby safeguarding public health.
The importance of Legionella risk assessment
Legionella risk assessment is essential for protecting public health, ensuring regulatory compliance, and managing safety risks effectively.
First and foremost, legionella risk assessment plays a vital role in public health protection by preventing outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease and safeguarding your business employees, customers, and communities. Identifying potential hazards allows for the implementation of effective control measures.
Moreover, regulatory compliance is another critical aspect, as many jurisdictions have specific regulations regarding Legionella control. A thorough risk assessment ensures adherence to these laws, avoiding potential legal issues.
Finally, in terms of risk management, identifying and addressing potential risks allows your organization to mitigate the likelihood of Legionella outbreaks. This proactive approach helps prevent the associated legal and financial consequences, ensuring a safer environment.
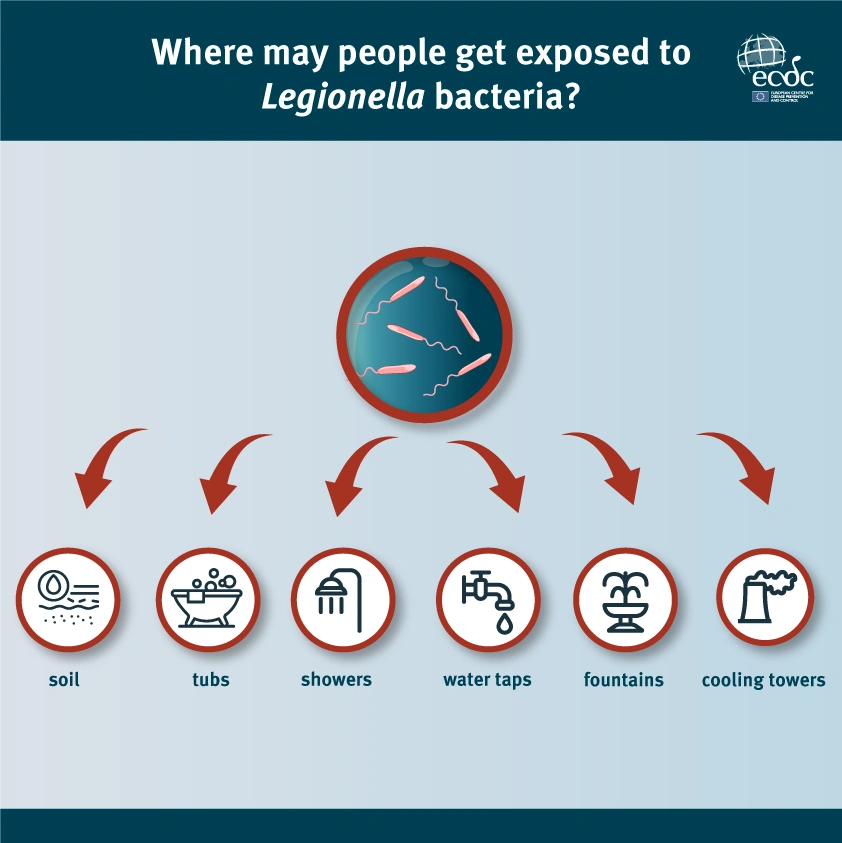
Identifying risk factors: Conducting a comprehensive Legionella risk assessment
A comprehensive Legionella risk assessment is essential for identifying and managing potential hazards in water systems. This process involves several key steps, including inventorying water systems, evaluating risks, and implementing mitigation strategies to ensure safety and compliance.
A comprehensive assessment includes:
- Inventory of water systems: Identify all water systems within the facility, including hot and cold water systems, cooling towers, humidifiers, and decorative fountains.
- Risk assessment: Evaluate each system for potential Legionella growth conditions, considering factors such as temperature, stagnation, nutrients, and aeration.
- Prioritization: Determine the level of risk associated with each system based on the likelihood of Legionella growth and the potential consequences of an outbreak.
- Mitigation strategies: Develop a plan to address identified risks. This includes ensuring hot water temperatures are maintained above 60°C (140°F) and cold water temperatures are below 20°C (68°F), using chemical disinfectants or shock chlorination for water treatment, and regularly cleaning and maintaining water systems to remove biofilms and scale. Implementing a monitoring and testing program is also crucial to assess the effectiveness of mitigation measures and detect early signs of Legionella growth.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of the risk assessment, mitigation strategies, and monitoring results.
These steps enable facilities to effectively manage Legionella risks, ensuring a safe and compliant environment.
Monitoring and testing
Regular monitoring and testing are essential for effective legionella control. This process involves several critical components to ensure that water systems remain safe and compliant.
To begin with, water sampling is a fundamental part of this process, requiring the collection of samples from various points within the water system to test for Legionella. Additionally, utilizing approved testing methods, such as culture-based techniques or molecular methods, is crucial for the accurate detection of the bacteria.
Furthermore, determining the appropriate testing frequency is important. This should be based on the level of risk associated with the specific water system and any relevant regulatory requirements. These steps collectively help in maintaining control over Legionella risks.
Compliance with regulations
Compliance with regulations is essential for effective Legionella control, ensuring safety and legal adherence. Key steps include understanding local requirements, implementing necessary measures, and seeking professional guidance.
First, understand local requirements by familiarizing yourself with specific Legionella control regulations in your jurisdiction. This helps identify the standards that must be followed. Next, ensure compliance by implementing measures that align with applicable regulations and standards. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and documentation are crucial for demonstrating adherence.
Additionally, seeking professional guidance is invaluable. Consulting with experts in Legionella control ensures compliance and enhances risk management through specialized knowledge.
These steps enable organizations to navigate the regulatory landscape confidently, ensuring safety and compliance in their Legionella control efforts.
Emerging trends and challenges
The field of Legionella control is rapidly evolving, presenting new challenges and opportunities. Understanding these trends is crucial for effective risk management.
To begin with, climate change affects Legionella growth conditions due to shifting climate patterns. Additionally, emerging strains may develop with different characteristics or treatment resistance.
Furthermore, technological advancements, such as water quality monitoring systems and rapid testing methods, significantly enhance control efforts. In healthcare facilities, unique risks require special precautions to protect vulnerable populations.
Lastly, cooling towers remain a common source of outbreaks, necessitating proper maintenance and disinfection. Staying informed about these trends enables organizations to adapt their strategies and ensure safer environments.
Case studies and best practices
Learning from real-world examples provides valuable insights into Legionella risk assessment and control. By examining successful prevention programs and analyzing factors contributing to outbreaks, organizations can identify best practices and avoid common pitfalls.
Case study 1: Industrial facility
A manufacturing facility in France faced challenges with Legionella concentrations in cooling towers. To address this, they implemented an ATP test kit to monitor and control microbial growth. This approach not only reduced the risk of Legionella but also saved the facility $250,000 by optimizing biocide usage.
Case study 2: Research and development facility
A research facility discovered Legionella in one of its cooling towers. They conducted thorough cleaning and disinfecting, followed by water sampling to confirm the elimination of the bacteria. This proactive management ensured the safety of the building’s occupants.
Case study 3: Educational institution
A University detected Legionella in two student halls during routine testing. They implemented flushing and cleaning protocols, ensuring no illnesses occurred. This case highlights the importance of regular maintenance, especially in vacant buildings(sms-environmental.co.uk)
These case studies highlight the importance of diligent monitoring and maintenance in preventing Legionella outbreaks across various sectors.
Best practices for Legionella control
Implementing best practices for Legionella control is essential for maintaining a safe and compliant environment. These practices help prevent outbreaks and ensure the health of all facility occupants.
- Regular maintenance: Regularly maintain water systems, including cleaning, disinfection, and inspection to prevent Legionella growth.
- Temperature management: Ensure that hot water temperatures are maintained above 60°C (140°F) and cold water temperatures are below 20°C (68°F) to inhibit bacterial proliferation.
- Water treatment: Use chemical disinfectants, shock chlorination, or other treatment methods to effectively control Legionella.
- Monitoring and testing: Implement a regular program to detect early signs of Legionella growth, ensuring timely intervention.
- Employee training: Provide staff with training on prevention and response procedures to enhance awareness and preparedness.
- Emergency preparedness: Develop an emergency response plan to address potential Legionella outbreaks swiftly and effectively.
Adhering to these best practices allows facilities to proactively manage Legionella risks, ensuring a safe and healthy environment for everyone.
Specific considerations for different industries
Legionella control strategies must be tailored to each industry due to unique challenges.
In healthcare facilities, vulnerable populations with weakened immune systems make Legionella control crucial.
Moreover, these facilities have complex water systems, including potable water, hot water, cooling towers, and humidifiers, all requiring careful management. Additionally, they must adhere to stringent regulatory requirements to ensure safety.
Similarly, hotels and resorts face different challenges, with their extensive water systems such as pools and spas. Ensuring guest safety is paramount, as Legionella outbreaks can severely damage a hotel’s reputation. Therefore, compliance with local and national regulations is essential to maintain safety standards.
In contrast, industrial facilities rely heavily on cooling towers, posing a significant risk for Legionella growth. Facilities that reuse water are at an increased risk of contamination, necessitating strict adherence to industry-specific regulations to mitigate potential hazards.
Finally, educational institutions must manage the risks associated with large populations of students, staff, and visitors. Water features like fountains and pools can harbor Legionella bacteria, making regulatory compliance vital to prevent outbreaks and ensure the safety of all occupant
Developing a comprehensive Legionella control program
Creating a robust Legionella control program is essential for ensuring safety and compliance in any facility. Incorporating key elements helps organizations effectively manage and mitigate risks associated with Legionella bacteria.
A comprehensive program should include:
- Risk assessment: Identify and assess potential Legionella risks within the facility.
- Mitigation strategies: Develop and implement effective measures to address identified risks.
- Monitoring and testing: Establish a regular program to ensure ongoing safety.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all control activities.
- Training and education: Provide staff with training on prevention and response procedures.
- Emergency preparedness: Develop a response plan to address potential outbreaks.
Integrating these components allows facilities to proactively manage Legionella risks, ensuring a safe environment for all occupants.
Advanced Legionella control techniques
Beyond standard mitigation strategies, organizations can enhance Legionella control by employing advanced techniques. Ultraviolet light disinfection effectively kills Legionella bacteria in water systems, providing an additional layer of protection. Silver ionization is another method, where silver ions inhibit the growth of Legionella and other microorganisms.
Additionally, ozone treatment can be used to disinfect water and reduce biofilm formation, further safeguarding water systems. Incorporating predictive analytics allows organizations to identify potential risks and proactively address them, enhancing overall control efforts. These advanced techniques provide robust solutions for managing Legionella risks.
In conclusion, Legionella risk assessment is vital for public health and safety. Understanding its risk factors and implementing effective mitigation strategies can significantly reduce the risk of outbreaks, safeguarding both occupants and the broader community.
Start your next assessments now with Lumiform
You’ve got this! With these Legionella risk assessment insights and your team’s support, you’re ready to enhance your safety protocols. Start today, knowing help is always available. Explore Lumiform’s platform, which offers powerful template creation tools, extensive libraries, and automation features.
Click here to use these resources to elevate your standards and audit other compliance areas in your business.
