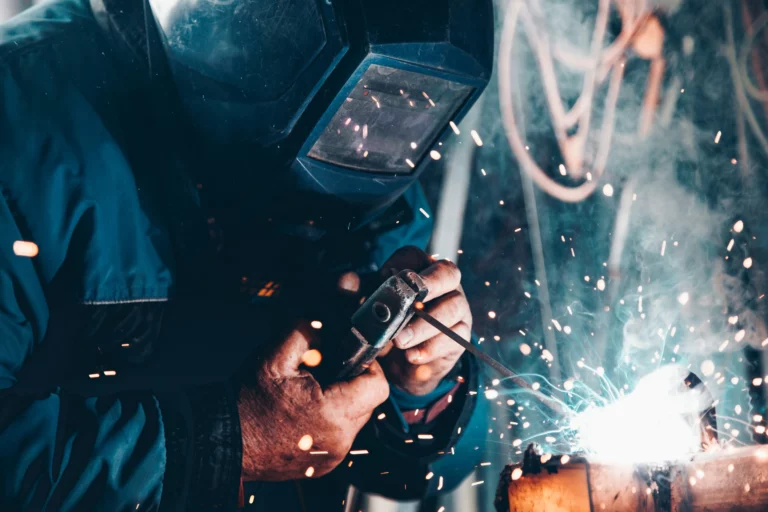
Safety is your top priority in any workplace, and welding is no exception. As you work in industries like construction, manufacturing, or oil and gas, you face unique hazards that demand careful management. Each year, many welders experience injuries and illnesses, including burns, eye damage, respiratory issues, and even fatalities.
Prioritizing welding safety is crucial—it protects your well-being, ensures the quality of your work, minimizes downtime, and prevents costly accidents. This guide offers a comprehensive understanding of welding safety, detailing essential equipment, best practices, regulations, and also common mistakes to avoid, empowering you to create a safer work environment.
Introduction to welding safety
Welding safety refers to the practices, procedures, and equipment used to protect welders and others in the surrounding area from the hazards associated with welding. This includes measures to prevent injuries and illnesses caused by exposure to arc rays, sparks, heat, and fumes, as well as electrical shock, fire, and explosions.
Effective welding safety requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, chemical, and biological hazards present in the welding environment.
Overview of common welding hazards
Welding involves various hazards that can pose significant risks if not properly managed. Some of the most common hazards include:
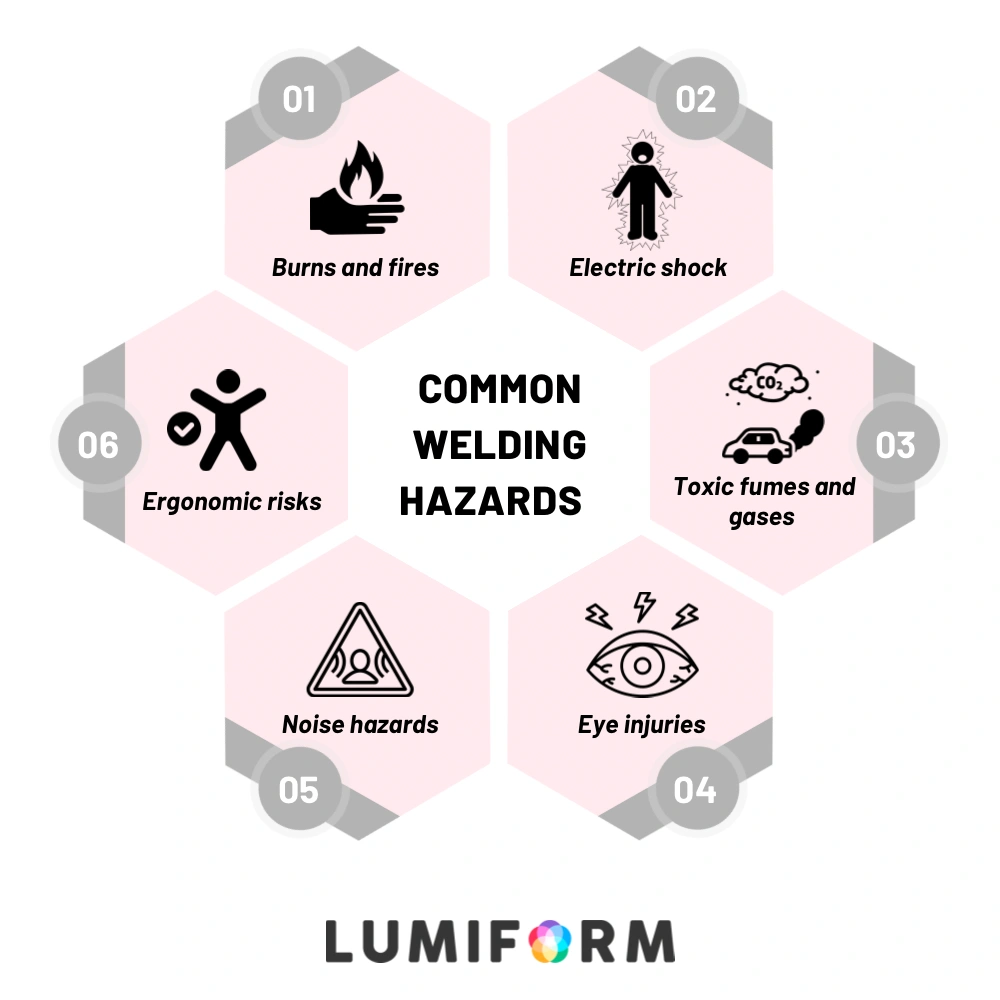
- Burns and fires: The intense heat generated during welding can cause severe burns. Sparks and molten metal can also ignite flammable materials, leading to fires.
- Electric shock: Welders work with electrical equipment that can cause electric shocks if not handled correctly. This risk is particularly high in wet or damp conditions.
- Toxic fumes and gases: Welding produces fumes and gases that can be harmful if inhaled. Prolonged exposure can lead to respiratory issues and other health problems.
- Eye injuries: The bright light and ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted during welding can cause eye injuries, including arc eye (welder’s flash) and cataracts.
- Noise hazards: Welding operations can produce high levels of noise, which can lead to hearing loss over time if proper hearing protection is not used.
- Ergonomic risks: Poor posture and repetitive movements during welding can cause musculoskeletal disorders, such as back pain and repetitive strain injuries.
Essential welding safety equipment
Ensuring safety in welding operations requires the use of appropriate equipment designed to protect welders from various hazards. This section outlines welding safety equipment that should be used to minimize risks and ensure a safe working environment.
- Welding helmets: Welding helmets protect the face and eyes from intense light, sparks, and UV radiation. They often come with auto-darkening filters that adjust the shade based on the welding arc’s brightness, providing continuous protection.
- Safety glasses and goggles: In addition to welding helmets, safety glasses or goggles should be worn to protect against flying debris and particles. They provide an extra layer of protection for the eyes.
- Protective clothing: Welders should wear flame-resistant clothing, such as jackets, aprons, and pants made from materials like leather or treated cotton. This clothing serves as a PPE against burns and sparks.
- Welding gloves: Heavy-duty welding gloves made from leather or other heat-resistant materials are essential for protecting the hands from burns, electric shock, and also, sharp objects.
- Respirators: Depending on the type of welding and materials used, respirators may be necessary to protect against inhaling toxic fumes and gases. However, respirators with appropriate filters should be selected based on the specific hazards present.
- Hearing protection: Welding operations can be noisy, so earplugs or earmuffs should be used to protect against hearing loss.
Welding safety regulations and standards
Adhering to welding safety regulations and standards is crucial for ensuring a safe working environment and avoiding legal issues. This section outlines the key regulations and standards that govern welding safety, also helping to provide a framework for compliance and best practices.
OSHA guidelines
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets forth regulations and guidelines to ensure the safety and health of workers involved in welding operations. Key OSHA guidelines for welding safety include:
- General industry standards (29 CFR 1910): OSHA’s general industry standards cover various aspects of welding safety, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilation, and also fire prevention. Specific sections relevant to welding include:
- 29 CFR 1910.252: General requirements for welding, cutting, and brazing.
- 29 CFR 1910.253: Oxygen-fuel gas welding and cutting.
- 29 CFR 1910.254: Arc welding and cutting.
- 29 CFR 1910.255: Resistance welding.
- Construction industry standards (29 CFR 1926): OSHA’s construction industry standards also address welding safety, with specific requirements for construction sites. Relevant sections include:
- 29 CFR 1926.350: Gas welding and cutting.
- 29 CFR 1926.351: Arc welding and cutting.
- 29 CFR 1926.352: Fire prevention.
- Hazard communication (29 CFR 1910.1200): OSHA’s hazard communication standard requires employers to inform workers about the hazards associated with welding materials and processes. This includes proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), and also training on hazard communication.
Industry-specific standards
In addition to OSHA guidelines, various industry-specific standards provide additional requirements and best practices for welding safety. Some of the key standards include:
- American Welding Society (AWS) standards: The AWS publishes a range of standards and guidelines for welding safety, including:
- AWS Z49.1: Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes. This comprehensive standard covers all aspects of welding safety, including PPE, ventilation, fire prevention, and electrical safety.
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards: The NFPA provides guidelines for fire prevention and protection in welding operations, including:
- NFPA 51B: Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot Work. This standard outlines fire safety practices and requirements for hot work operations.
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards: ANSI publishes standards related to welding safety, including:
- ANSI Z87.1: Occupational and Educational Personal Eye and Face Protection Devices. This standard specifies requirements for eye and face protection devices used in welding.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards: ISO provides international standards for welding safety, including:
- ISO 15011: Health and Safety in Welding and Allied Processes. This series of standards addresses various health and safety aspects of welding, including ventilation and exposure to hazardous substances.
Common welding safety mistakes and how to avoid them
Despite the availability of comprehensive guidelines and safety measures, common mistakes can still occur during welding operations. Identifying these mistakes and understanding how to avoid them is proper for maintaining a safe working environment. This section outlines some of the most frequent welding safety mistakes and provides strategies to prevent them.

- Inadequate training: One of the most significant mistakes in welding safety is insufficient training for welders and other personnel involved in welding operations. This can lead to improper handling of equipment, incorrect welding techniques, and a lack of awareness about potential hazards. To avoid this, it is essential to provide comprehensive training that covers both theoretical and practical aspects of welding techniques, equipment use, and safety protocols.
- Ignoring safety protocols: Neglecting established safety protocols, such as not wearing proper personal protective equipment (PPE) or bypassing safety checks, can lead to accidents and injuries. To prevent this, companies should enforce strict safety policies that clearly outline the required PPE, equipment checks, and safety procedures. Also, managers can conduct regular safety audits to help ensure compliance with these protocols, and address any violations immediately with corrective training if necessary.
- Improper use of equipment: Using welding equipment incorrectly or failing to maintain it properly can result in equipment malfunctions, accidents, and poor-quality welds. To avoid this, it is important to ensure that all welders receive proper training on the correct use and maintenance of welding equipment. This training should be specific to the different types of welding machines and tools used. Regular maintenance schedules should be implemented for all welding equipment, and inspections should be conducted before each use to identify and address any issues.
- Inadequate ventilation: Poor ventilation in the welding area can lead to the accumulation of toxic fumes and gases, posing serious health risks to welders. To prevent this, proper ventilation systems should be in place, including local exhaust ventilation systems that capture and remove fumes at the source. Also, regular monitoring of air quality in the welding area is necessary to ensure that ventilation systems are functioning effectively. This can be possible through the use of air quality sensors and periodic air sampling.
- Failure to conduct pre-welding inspections: Skipping pre-welding inspections can result in unrecognized hazards, such as flammable materials or faulty equipment, leading to accidents. To avoid this, thorough inspections of the welding area, equipment, and materials is important before starting any welding operation. Using pre-welding inspection checklists can help ensure that all necessary checks are consistent with the welding process. Involving multiple personnel in the inspection process can also provide additional oversight and catch any potential issues that may rise later.
Ensure workplace safety: Try Lumiform for welding safety
As you navigate the complexities of welding safety, remember that protecting yourself and your colleagues is paramount to maintaining a secure and efficient workplace. By adhering to best practices, utilizing proper equipment, and staying informed about regulations, you significantly reduce risks and enhance the quality of your work.
Lumiform offers robust tools and templates to help streamline your workplace safety processes, ensuring thorough inspections and compliance checks.
Explore Lumiform to empower your team with the resources needed to uphold safety standards and foster a productive work environment. Sign up for FREE here!

